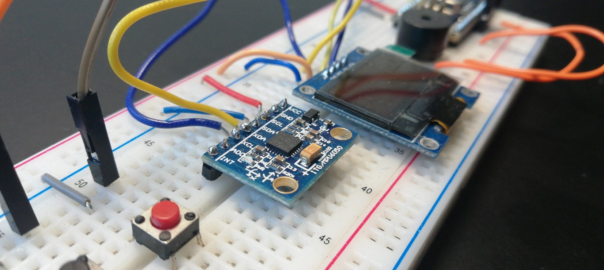
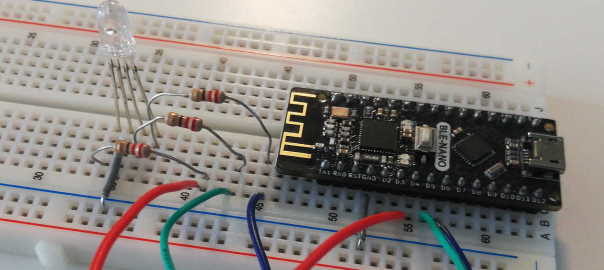
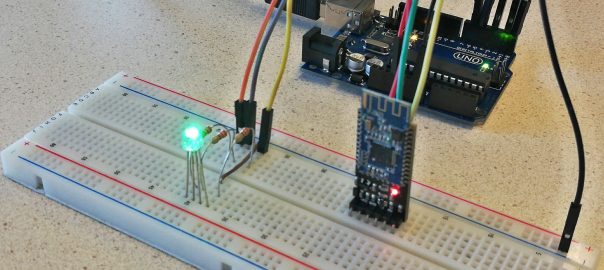
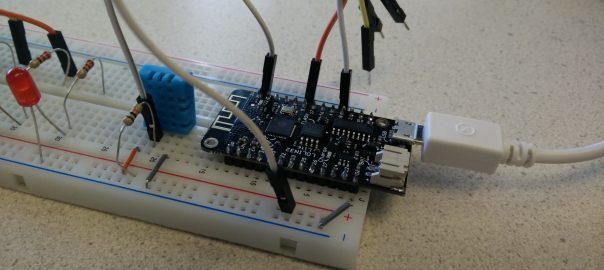
In this tutorial, we are going to create a gamecontroller which can control the game using movements. By tilting the gamecontroller, you can control the movement of the basket. We will extend the game made in the previous tutorial. Carrying out the assignment Realizing the gamecontroller can be done in 2 ways: Using the MPU-6050 Accelerometer … Continue reading Tutorial: Create a gamecontroller for the catch-the-ball game →
This tutorial describes how to build an electronic circuit with an RGB LED (a LED that can change color), and change its color using an App. It also demonstrates two-way communication over Bluetooth LE between an App built with App Inventor and the BLE-Nano board. The BLE-Nano board is basically an Arduino Nano with an … Continue reading Bluetooth communication between an App built with App Inventor and the BLE-Nano board →
Most examples in this article use an OLED display. Countdown timer example In its simplest form, a countdown timer can be coded like this, using the loop() for repetition (no for- or while-loop needed!): Download the sketch: oled_display_countdown_start_button.ino Full simulation including breadboard on Wokwi: This will countdown from 10 to 0 in ten seconds after … Continue reading Countdown timers and executing tasks in parallel on an Arduino →
The BLE-Nano as sold here is a combination of a traditional Nano with a Bluetooth BLE module, based on the CC2540 BLE bluetooth chip. The Bluetooth module is directly connected to the TX, RX pins of the Arduino (pins 0 and 1). There is a troubleshooting section further down on this page! This is the … Continue reading Introduction to the Arduino BLE Nano →
Learn how to build a remote controlled Rover car with Lego Mindstorms, with an Arduino ‘brain’, which can be remote controlled via Bluetooth with a phone. This guide uses parts from the Steering rover example on nxtprograms.com. It is also inspired by the NXT Dune Buggy.Lego parts shown here might be of different color depending … Continue reading Lego: Build remote controlled Rover car with Arduino brain →
Pages with slides of presentations of recent workshops: 03-12-2020 Industry 4.0 Sensor Workshop 18-11-2020 HTHT Science 2 Society Prototyping workshops 11-03-2020 Prototyping for Project Design for Specific Users Previous/older workshops: LittleBits workshop
In this example we will control a RGB LED from an Android App via a Bluetooth connection. A HM10 BLE Bluetooth module is connected to an Arduino Uno. This tutorial assumes you already have some experience with Arduino. If not, you might want to follow a basic tutorial and/or install the Arduino software (the IDE). … Continue reading Control an RGB LED from an Android App via Bluetooth →
To quickly change the Spike into an Explorer robot, you can strip legs, claws and tail, leaving the chassis as a basis to build the Explorer robot.Then add wheels, a bumper with touch sensor and an ultrasonic sensor mounted on a motor. You can also build the Explorer from scratch, then you can follow the … Continue reading Lego: use Spike chassis to build Explorer robot →
This guide explains how to build the Lego Mindstorms model “Spike”, powered by an Arduino and an EVShield. The original version of the Spike is powered by a Lego NXT. Requirements EVShield, Arduino Uno, Battery holder (+6 AA batteries) Lego Mindstorms kit (can be either NXT or EV3) Introduction To make a sturdy, compact solution … Continue reading Lego: Build Spike with Arduino brain →
The ESP32 Wifi module can replace an Arduino, as it has similar properties. It’s main advantage is that it is faster, has more memory and has WiFi and Bluetooth on board. Just like the Arduino Nano it can be mounted on a breadboard. This allows building very compact prototype circuits: Make module ready for use … Continue reading Getting started with the ESP32 Wifi module →