This tutorial describes how to build an electronic circuit with an RGB LED (a LED that can change color), and change its color using an App. It also demonstrates two-way communication over Bluetooth LE between an App built with Android Studio. Older versions of this tutorial: If you have and Arduino, that can also work … Continue reading Create an RGB Led controller App →
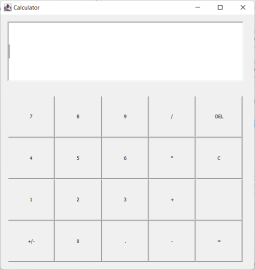
In this tutorial, we will create a simple text-based calculator. It’s meant to practice basic Java syntax, like println(), if- and basic arithmetic. The resulting calculator can only do the 4 basic operations and it does not recognize fractions. It is advised to first go over a basic tutorial like on w3schools.com/java before attempting this … Continue reading Learn Java basics with a simple calculator →
Learn how to create a simple calculator in Java.
In this tutorial, you will make a simple game in which balls are launched, which we then have to catch. The user of the game controls a basket in which the balls must be collected. The aim is to catch as many balls as possible and earn points that way. The basket is located at … Continue reading Java tutorial: Programming a Catch-the-ball game →
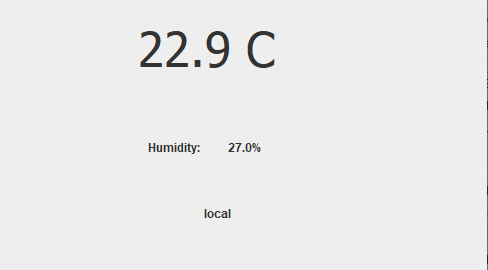
This article assumes you have already some experience in creating Java Apps. For instance if you have done the first 2 lectures of the course Application Development. You should also have prepared the DHT temperature/humidity sensor and have a working sketch for it (eg. by completing step 1 and 2 of practical assignment 2 of … Continue reading Create a stand-alone Java App that displays info from a connected sensor →
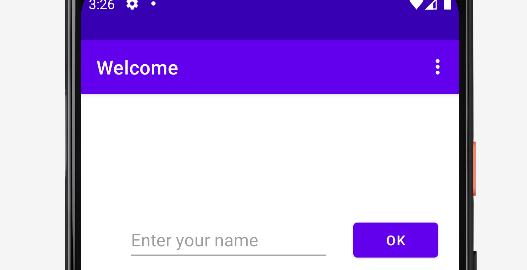
Part of series about Android App Development. This is the second article, in which you will learn to create a first interactive userinterface.
Part of series about Android App Development: first step: installing Android Studio and create a ‘hello world’ app.
To show your processing creation in a webpage (or WordPress post or page*) you can use the example code below. * in WordPress, add a Custom HTML block (or switch to HTML-mode) to enter HTML-code in a post or page. Please take note of the following: Including scripts like this only works online (hosted on … Continue reading Include a processing file (.pde) in a webpage →
Sometimes I get a question from a student or colleague on why we choose Java as our base for the introduction to programming classes. Here are some quick reasons: It is a ‘proven’ language to quickly learn programming It is used as first learned programming language in a lot of other universities and high schools It … Continue reading Why learn programming with Java? →
Update March 2025: Until 2024, this course was part of module “Smart Products” of the programme Industrial Design Engineering. Its main focus was on learning programming with a focus on prototyping smart products. Starting September 2025, a new course “Design of Data Acquisition Systems” will be introduced for module “Data Driven Design”, which will have … Continue reading Application Development →